PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
What is a bidirectional glass fiber and glass wrap?
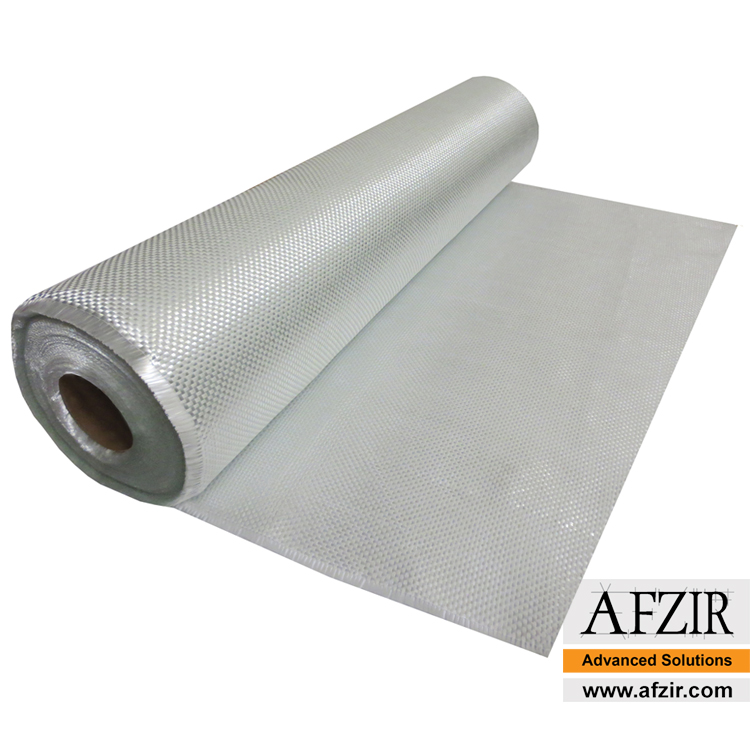
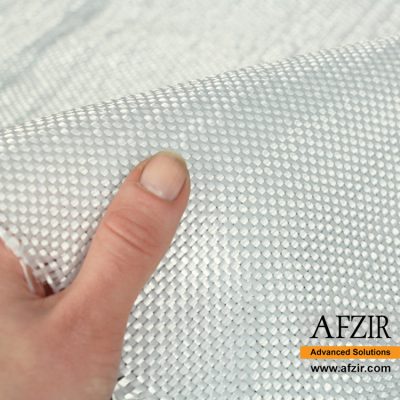
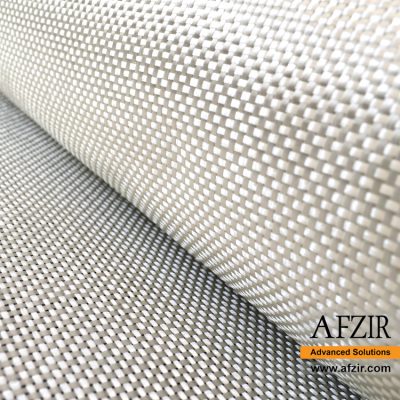
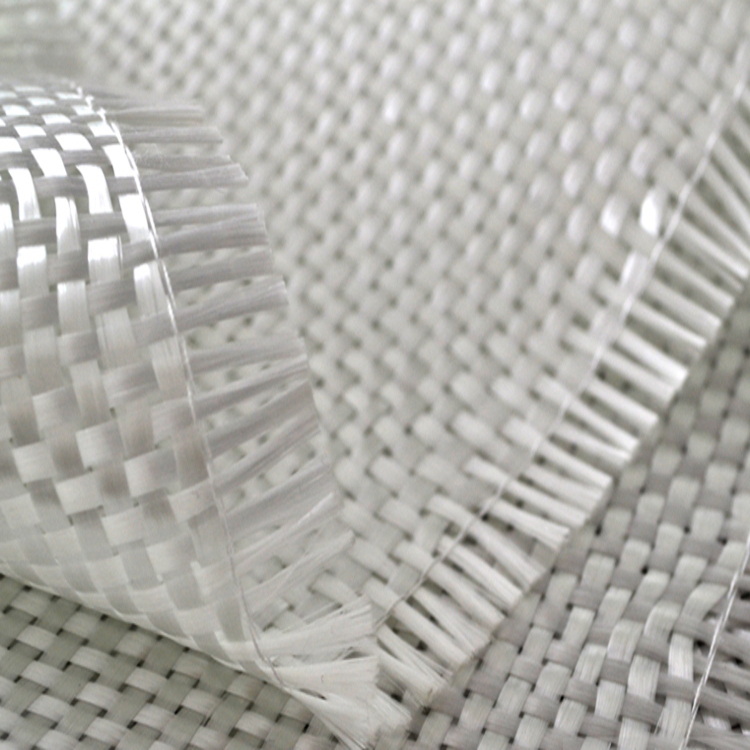
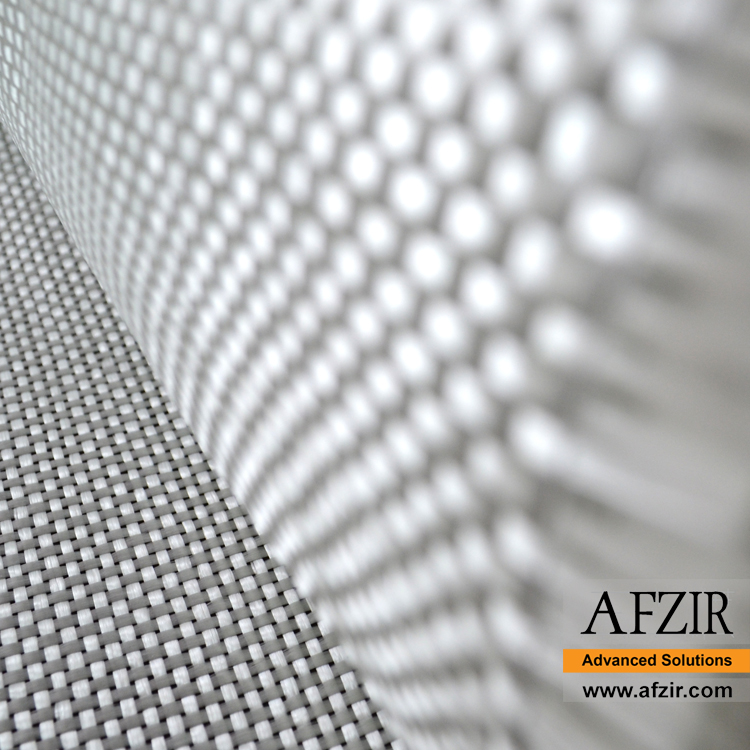
A bidirectional glass fiber and glass wrap are reinforcing fabrics made of glass fibers that are stronger and perform better than unidirectional glass fibers, without adding extra weight or thickness. Glass fiber fabric has been widely used in various forms and is a popular choice for reinforced composites. These fabrics come in different types, offering a range of properties including high strength and fire resistance at an affordable cost. The yarn sizes and weave patterns allow for flexible design options.
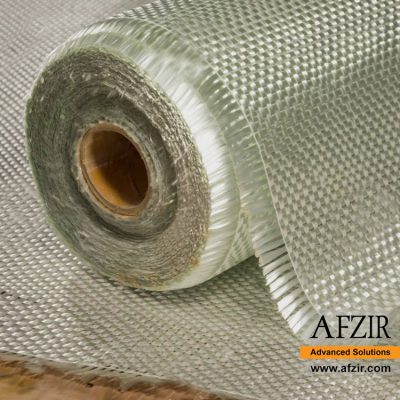
Afzir’s bidirectional glass wraps are woven in weights ranging from 200 to 900 grams of fibers. These glass fibers can be combined with resins like polyester or epoxy to create rigid plastic composites. The bidirectional glass wrap is suitable for wet lay-up, vacuum bag, and resin injection methods, and can be used alone or in combination with other reinforcements like carbon fibers. It finds applications in RC wings, car panels, surfboards, boats, and molding. It is a great alternative to traditional short-fiber fabrics, especially when working with epoxy resin.
Different Types of Bidirectional Glass Fibers:
There are different types of bidirectional glass fibers used according to project needs:
- Class E glass fibers: Commonly used fibers with low alkali content. Used for retrofitting structures and in the electrical industry as resistors.
- Class C glass fibers: Used in environments with corrosive chemicals.
- Class A glass fibers: No longer in production.
- Class S glass fibers: High strength and modulus of elasticity. Mostly used in the aerospace industry to cover missiles and aircraft parts.
Applications of Bidirectional Glass Wrap:
Bidirectional glass wrap is used for retrofitting and repairing pipes, tanks, historical buildings, arches, tunnels, and highways. It reinforces surfaces damaged by fire or extends the lifespan of structures. It enhances the seismic resistance and load capacity of masonry or concrete shear walls, beam and column joints, and compensates for design problems in concrete beams, slabs, columns, and walls.
The use of bidirectional glass wrap improves the hardness of high-performance structural laminates without adding weight or thickness. It is also used as a reinforcing material in high-pressure laminates for printed circuit boards (PCBs) in computers, modems, automobiles, and telecommunication products.
Difference between Bidirectional Glass Fabric and Bidirectional Carbon Fabric:
- Glass fabric has a lower tensile modulus than carbon fabric.
- Glass fabric has a lower specific gravity than carbon fabric.
- Glass fabric has lower fatigue resistance.
- Glass fabric is harder and slows down cutting tools.
- Glass fabric is cheaper than carbon fabric.
- The tensile strength of glass fabric is lower than that of carbon fabric.
What is the purchase price of Bidirectional Glass Fabric?
The price of bidirectional glass fabric is calculated per meter. To get more information and the current price, you can contact our experts.
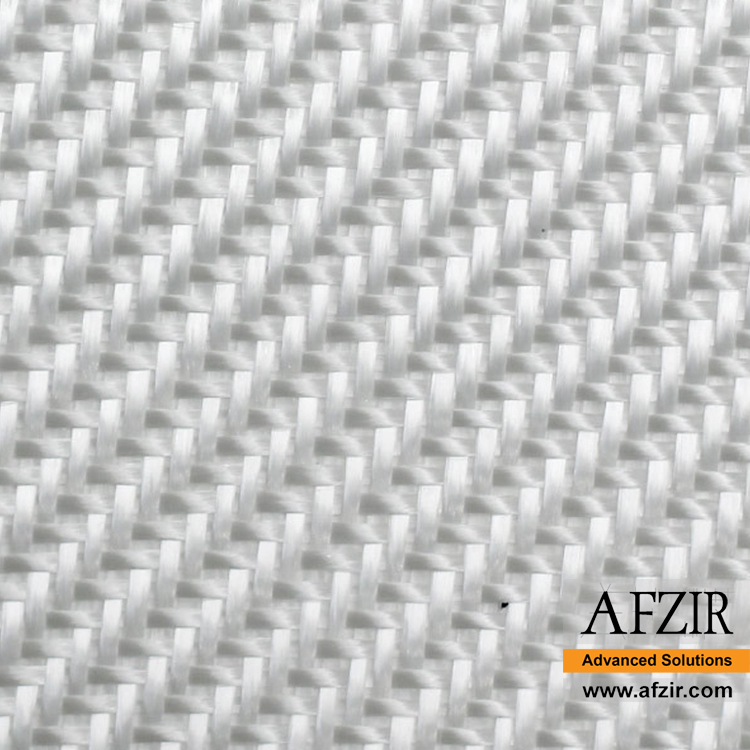
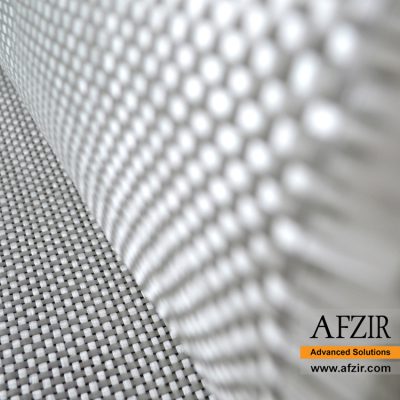
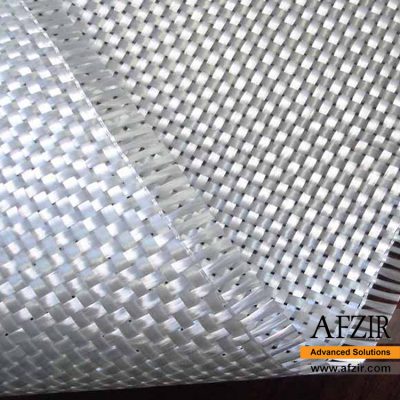
Specifications of Bidirectional Glass Wrap:
Bidirectional glass fabrics have perpendicular warp and weft, providing higher tensile strength than steel. Their tensile modulus is around 70 GPa. They can be used as external reinforcement and are resistant to corrosion and acidic environments.
Parameters to Consider Before Buying Glass Fiber:
- Softness or denier of fibers.
- Fabric weight (weight per unit area).
- Overall thickness.
- Overall width or outside diameter (OD).
- Overall length (varies based on customer’s order).
Key Features
- Strong and lightweight fabric
- Cures at ambient temperature
- Non-corrosive glass fiber wrap
- Flexible fabric
- Low aesthetic impact
- Compatible with various finishes
Applications
- Seismic retrofitting and strengthening of structures
- Enhancing load-carrying capacity of structural components
- Repairing damaged structural elements
- Remedying defects in structures
- Mitigating blast effects on structures
- Retrofitting bridges and silos
- Sealing tanks and applying industrial coatings and FRP lining
- Manufacturing GFRP composite components
Packaging
- Weights 100-1200 grams per square meter and width 50-100 mm
Colour
- white
technical specifications
| Arial Weight |
200-880 gr/m² |
| Fabric Thickness |
0.16-0.34 mm |
| Weave Pattern |
bidirectional |
|
Primary Fiber Direction |
0° and 90° |
|
Width (mm) |
50-100 mm |
|
color |
white |
|
Comparison of properties of bidirectional glass fiber with conventional construction steel |
||
|
parameter |
Bidirectional fiber |
steel |
| Tensile Strength | 2500 MPa |
360 MPa |
| Tensile Modulus | 70 GPa |
200 GPa |
|
Density |
2550 Kg/m³ |
7850 Kg/m³ |
|
Corrosion resistance |
Yes |
No |
|
Acid resistance |
Yes |
No |
Reinforcing structures aims to increase bearing capacity, address corrosion and erosion issues, enhance ductility, adapt structure usage, and rectify design and construction errors.
Bidirectional glass fibers are commonly used for seismic retrofitting and improvement projects due to their corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and lightweight properties.
Before implementing reinforcement, a thorough examination of the structure is necessary, including assessing bearing capacity, defects, structural calculations, and existing documentation.
Design Principles of Bidirectional Glass Fiber Reinforcement: Design follows limit state principles for acceptable performance and safety. Strength reduction coefficients are applied due to less familiarity with FRP composites compared to other materials like concrete. A design reliability coefficient of over 3.5 is recommended. Material properties, such as compressive strength and modulus of elasticity, should be determined through tests like core drilling, compressive strength testing, and ultrasonic testing.
Behavior of Bidirectional Glass Fibers:
Tensile Behavior:
Bidirectional glass fibers exhibit linear stress-strain relationship until sudden failure. Fiber type, orientation, and amount significantly affect tensile strength and hardness.
Compressive Behavior:
Bidirectional glass fibers should not be used as compression reinforcement in outer coverings, but they can indirectly increase the capacity of columns due to their confinement behavior.
Evaluation and Acceptance:
Evaluation includes checking fiber direction, layer separation, adhesion to surfaces, and compliance with design drawings. A supervisory body oversees this process. Laboratory information from the supplier company guides material control.
After installation, the adhesive tensile test (Pull-Off test) should be conducted on core samples to ensure adhesive resistance exceeds 1.4 MPa. If the system fails or separates from the concrete, it indicates defects.
Other considerations for evaluating and approving installed fibers include checking for separation, correct layer placement, post-curing thickness, and fiber splice length.
Rehabilitation goals
Bidirectional glass fibers are widely used in various industries due to their mechanical properties comparable to carbon fibers and polymers.
The main purpose of retrofitting is to enhance a structure’s resilience against various forces, particularly earthquakes. However, retrofitting can also address other issues like changing building usage and the deterioration of materials.
It applies to two types of buildings: existing and in-use structures, as well as earthquake-damaged buildings. Retrofitting is gaining importance due to the high cost and time associated with demolishing and replacing existing buildings.
Requirements for Building Retrofitting:
The following cases necessitate the development and implementation of retrofitting plans:
1. Existing damage in old buildings:
Common building issues such as honeycombing, abnormal cracks, and corrosion of rebars in concrete structures often go unnoticed and require concrete testing methods like corrugation and rebar scanning.
2. Executive errors:
Mistakes made during construction, such as weak concrete specimens, inconsistencies in design strength, beam and column buckling, and honeycombing, need to be addressed by retrofitting experts.
3. Change of building use:
When buildings undergo changes in their purpose, it’s essential to conduct a thorough examination by experts. Altering building usage creates new forces that the structure may not have been designed for, potentially leading to severe damage to load-bearing members. Consulting engineers must evaluate the existing structure and assess the feasibility of the proposed change of use to provide an accurate and detailed plan.
Detecting defects in a timely manner and selecting the appropriate solution can save significant costs. It is crucial to seek assistance from experienced professionals in the field to avoid exacerbating structural issues.
Implementation of Bidirectional Glass Fibers:
The implementation details of bidirectional glass fibers depend on factors such as the structure’s geometry and substrate smoothness. Contractors must adhere to the specifications provided by the consulting engineer, including the type of fibers, resin, number of layers, and execution method, to ensure proper reinforcement operations.
Steps for Implementing Bidirectional Glass Fibers:
To achieve the desired quality, the following steps should be followed carefully during the implementation of bidirectional glass fibers:
1. Concrete repair and substructure preparation:
Before applying the fibers, all defects in the main concrete and underlying concrete that may impact the integrity of the CFRP composite should be eliminated. Additionally, if there is a risk of rebars corroding or rusting in the concrete, proper cleaning and repair should be carried out.
2. Mixing resins:
Resins must be mixed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and project specifications. All resin components should be mixed at the appropriate temperature and in sufficient quantity to ensure proper material consistency.
Various Methods for Installing Bidirectional Glass Fibers:
Once the substrate is prepared, bidirectional glass fibers can be installed using different methods, as specified by the consultant. Here are some installation approaches:
a. Bidirectional glass fiber wet gluing system:
In this method, the fiber system is manually installed using wet resin. The fibers can be impregnated separately with resin materials using a device and then applied to the concrete surface.
b. pre-impregnated fiber system:
Pre-impregnated bidirectional systems are already impregnated with resin at the factory but not cured. These fibers are bonded to surfaces with or without additional resin and cured on-site.
Non-compliance with the consultant’s instructions and manufacturer’s guidelines can lead to weakened system strength or fiber detachment from the surface. Some key considerations include avoiding sticking bidirectional glass fibers to inner corner surfaces as much as possible, ensuring sufficient development length, and applying overlaps in patched areas.
After implementing the FRP system, it is essential to establish quality assurance and control programs led by the quality control unit (QC). Quality control involves conducting necessary inspections and tests.
Quality control inspectors should have a comprehensive understanding of the FRP system and its installation.
During the installation of the unidirectional glass fiber system, daily inspections should cover the following aspects:
- Ambient temperature, relative humidity, and weather conditions.
- Surface dryness.
- Surface preparation methods.
- Observation of resin curing process.
- Detection of layer separation or air bubbles.
The quality control unit should also conduct periodic inspections and evaluations of the implemented CFRP composite.
Evaluation Methods for FRP Systems:
1. General inspections:
Visual inspections are conducted to identify changes in color, fiber separation, or cracking, which indicate weaknesses in the system and improper execution. Surfaces covered with FRP materials should be regularly monitored and inspected.
2. Evaluation of concrete composite material separation:
Separation of concrete composite materials in FRP systems is a critical failure. Periodic pull-off tests should be performed to diagnose this condition according to regulations. If minor damage is detected, cautious methods like resin injection can be used for repairs. For more significant damage, such as scaling or layer separation on a larger scale, defective materials may need to be removed. The cleaned area can then be recoated with new materials.
3.Long-term Monitoring and Inspection:
Similar to other structural members, the unidirectional glass fiber reinforcement system requires ongoing monitoring and inspection. Bridge inspections are generally conducted annually and, in more detail, every six years. However, regular inspections for buildings are less common. Building quality control engineers should justify the need for regular monitoring and inspection of reinforced members, especially in CFRP composite reinforced buildings.
technical documents
Photo Gallery
Technical documentation request
Frequently Asked Questions
What are bidirectional glass fibers?
Double-sided fiberglass fabrics are made from high-strength fiberglass liners that are interwoven in the form of blur (0 and 90 degrees). Bidirectional fiberglass fabrics are compatible with resins such as epoxy resin, vinyl ester resin and polyester resin. Combining this type of fabric with compatible resins can provide parts or composites with excellent mechanical properties, in addition to the two-dimensionality of the fibers in these fabrics, the mechanical properties of the fibers are provided at distances of 0 and 90 degrees.
What is the brand of bidirectional glass fibers?
The brand of each product is determined by the manufacturer. The brand of bidirectional glass fibers is usually abbreviated to English. For example, double-sided glass fibers are known in Afzir Retrofitting Company under the trade code BGWTM.
What is the special advantage of bidirectional glass fibers?
The special advantages of these fibers include high tensile strength, reasonable price compared to other fibers, high chemical resistance, low weight, high heat resistance, etc.
What is the price of bidirectional glass fibers?
The price of bidirectional fiberglass fabric is lower than that of carbon fiber fabric. Because it has relatively less technical specifications than carbon fiber fabrics. The price of bidirectional glass fibers is determined based on the required weight and dimensions. Due to market fluctuations, it is not possible to offer a single price. For this purpose, to inquire about the daily price of the product, you can contact our experts in Afzir Company.
What are the uses of bidirectional glass fibers?
bidirectional glass fibers in seismic reinforcement and improvement of buildings, retrofitting of industrial structures, retrofitting of bridges and silos, retrofitting of pipes and tanks, sealing of tanks and industrial coatings, manufacture of FRP composite parts, etc...
How to make bidirectional glass fibers?
bidirectional fiberglass fabrics can be sourced from companies that provide reinforcement materials, such as Afzir company.
What is the type of glass used in bi-directional fiberglass fabrics?
bidirectional fiberglass fabrics are widely produced with E-Glass. But it can be made according to customer needs with types of glass type A, type AR glass, type S glass and type C glass.
What surfaces are bidirectional glass fibers compatible with?
bidirectional glass fibers are compatible with surfaces such as concrete, steel, wood and plastic and are well installed on them.
In what dimensions and weights is bidirectional fiberglass fabric available in the market?
bidirectional fiberglass fabrics are marketed in weights of 200 to 1200 g per meter and in widths of 50 to 100 cm. In general, heavy glass fibers are heavier than carbon fibers.
What resins are bi-directional glass fibers compatible with and in what ways can they be applied?
bidirectional fiberglass fabrics are compatible with resins such as epoxy resin, vinyl ester resin, polyester resin, phenolic resin and polyurethane resin. Double-sided fiberglass fabrics can be made by methods such as pre-impregnated system, wet gluing system, resin transfer molding system, compact molding system, etc.








































Be the first to review “Bidirectional Glass Wrap”