PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Is AFRP Aramid Fiber the Ideal Solution for Various Applications?
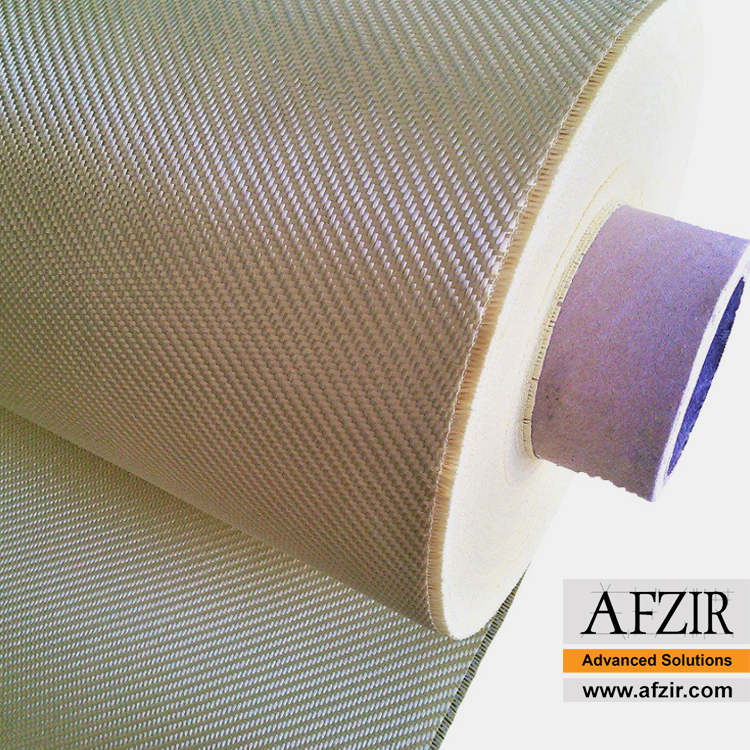
AFRP Aramid Fiber AFRP Aramid Fiber, also known as Kevlar, is a versatile material with exceptional properties that make it suitable for various applications. Its high heat resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability set it apart in the market. This fiber offers unparalleled performance and reliability, from protective clothing to structural reinforcement.
Are Nomex and Kevlar Transforming the Field of Aramid Fibers?
From Nomex to Kevlar, Introduced by DuPont in the 1960s, AFRP Aramid Fiber quickly gained recognition under the brand Nomex for its remarkable heat resistance. Further research led to the development of Kevlar by chemist Stephanie Kulk in 1973. Kevlar has become the industry standard for aramid fibers, known for its exceptional strength and durability.
How Does Aramid Fiber Unidirectional Fabric Revolutionize Reinforcement?
Revolutionizing Reinforcement AFRP Aramid Fiber’s unidirectional fabric has revolutionized the field of reinforcement. With excellent mechanical properties, including resistance to bending, shearing, compression, seismic forces, and wind, this fabric enhances the durability and performance of structures. Its ability to control fissure extension, increase flexibility, and withstand harsh external environments sets it apart from traditional methods.
Can Aramid Fiber Unidirectional Fabric Protect Structures from Chemical Erosion?
Protecting Structures The excellent chemical stability of Aramid Fiber’s unidirectional fabric makes it highly resistant to erosion caused by acids, alkalis, salts, and ultraviolet light. This stability ensures the long-term protection and preservation of reinforced and repaired structures. Moreover, the fabric’s adaptability to climate changes allows for easy application of fire-retardant coatings, reducing the risk of fire-related incidents.
Do Lightweight Kevlar Fibers Offer a Strong Advantage in Performance?
Kevlar’s Advantage Kevlar fibers, lighter than carbon and glass fibers, offer the highest tensile strength-to-weight ratio. They are approximately 43% lighter than glass fibers and 20% lighter than carbon fibers. This advantage, coupled with its toughness and impact resistance, makes Kevlar an excellent choice for various applications, including bulletproof vests. The exceptional properties of Kevlar have made it one of the most successful applications of aramid fibers.
What Mechanical Performance Can Kevlar Fibers Provide in Different Stresses?
Tensile and Shear Strength Kevlar fibers, exhibit impressive mechanical performance. Kevlar proves its reliability in demanding conditions with a tensile strength of approximately 55% of that of glass fibers and a shear strength of 180% of that of glass fibers. While its tensile strength is slightly lower than that of carbon fiber, its overall performance and behavior under different stresses make it an ideal choice for various applications.
How Do Aramid Fibers Handle UV Exposure and Chemical Reactions?
Preserving the Integrity UV light poses a challenge to aramid fibers, but composite structures mitigate this by providing protective layers. Matrix resins play a crucial role in shielding the fibers, and adding UV absorbers further enhances protection. Kevlar fibers exhibit a minimal reaction to organic solvents and aqueous solutions, but precautions must be taken when exposed to strong acids and bases in high temperatures or concentrations.
In What Forms Can Aramid and Kevlar Fibers Be Utilized?
From Yarn to Short Fibers, Aramid and Kevlar fibers are available in various forms such as yarn, spun fabrics, and short fibers. These versatile options cater to application requirements and enable seamless integration with existing materials and structures. Due to their unique properties, specialized cutting tools are necessary for working with aramid fibers.
What Are the Market Value and Cost Considerations of Aramid Fibers?
Numerous advantages that aramid fibers offer. While the cost may limit their widespread use in structural applications, the specialized nature of these fibers makes them highly sought after in specific industries. Aramid fibers’ exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability make them indispensable in critical fields such as aerospace, defense, and protective gear. The market demand for Kevlar fibers continues to grow as more sectors realize the unique benefits they provide regarding safety, reliability, and performance. As research and innovation in aramid fiber technology progress, there is potential for cost reductions, making these fibers even more accessible in the future.
Key Features
- Excellent ratio of tensile strength and modulus to weight
- High impact resistance
- Good fatigue resistance
- Good resistance to acids and bases
- Excellent resistance to corrosion failure and cracking
- Resistant to organic solvents such as fuels and emollients
- Good vibrational energy dissipation and vibration damping
- Can be used continuously up to 180 degrees Celsius
- Self-extinguishing with low smoke properties in case of fire
Applications
- Retrofitting and strengthening structural elements in construction projects
- Manufacturing military bulletproof vests
- Constructing military armored vehicles
- Producing uniforms for police officers and security guards
- Firefighting suits
- Car racing drivers’ uniforms
Packaging
- –
Colour
- yellow
technical specifications
Here are some suggestions for engineers working with Aramid fiber:
Understand the properties: Familiarize yourself with the specific physical and mechanical properties of Aramid fiber, such as its tensile strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. This will help you effectively design and engineer applications that leverage these unique characteristics.
Consider application requirements:
Assess the specific requirements of your application, such as load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and desired performance. Determine how Aramid Fiber can meet those requirements and provide suitable solutions.
Conduct thorough testing:
Before implementing Aramid fiber in a project, conduct comprehensive testing to evaluate its performance and durability under relevant conditions. This will ensure that the material meets the necessary standards and provides the desired outcomes.
Proper material handling and storage:
Aramid fiber is known to absorb moisture, so it’s crucial to handle and store the material carefully to prevent moisture absorption. Follow manufacturer guidelines for storage conditions and ensure proper protection during transportation.
Consider compatibility with other materials:
If using Aramid fiber in composite materials or hybrid structures, consider the compatibility and bonding characteristics with other materials. This will help optimize the overall performance and integrity of the final product.
Collaboration with material suppliers:
Engage with reputable Aramid fiber suppliers or manufacturers to gain insights into the latest advancements, application-specific recommendations, and potential material limitations. This collaboration can also provide valuable support during the design and development stages.
Adhere to safety guidelines:
like any other material, Aramid fiber may have specific safety considerations. Ensure that you and your team are well-informed about the safety guidelines, proper handling procedures, and any potential health risks associated with working with Aramid fiber.
Continuous learning and research:
Stay updated with the latest developments, research, and innovations related to Aramid fiber. Attend conferences, workshops, and industry events to network with experts and gain valuable knowledge to enhance your understanding and application of the material.
Remember, proper understanding, meticulous planning, and adherence to best practices are essential for successful engineering projects involving Aramid fiber.
Understand the properties:
Familiarize yourself with the physical and mechanical properties of Aramid fiber to effectively utilize its unique characteristics in engineering applications.
Consider application requirements:
Assess the specific needs of your project and determine how Aramid Fiber can meet those requirements to provide suitable solutions.
Conduct thorough testing: Before implementing Aramid fiber, perform comprehensive testing to evaluate its performance and durability under relevant conditions.
Proper material handling and storage:
Handle and store Aramid fiber carefully to prevent moisture absorption, following manufacturer guidelines.
Consider compatibility with other materials:
Assess the compatibility and bonding characteristics of Aramid fiber with other materials in composite or hybrid structures.
Collaboration with material suppliers:
Engage with reputable Aramid fiber suppliers to gain insights and support during the design and development stages.
Adhere to safety guidelines:
Follow safety guidelines, proper handling procedures, and health risk considerations associated with working with Aramid fiber.
Continuous learning and research: Stay updated with the latest developments, research, and innovations related to Aramid fiber to enhance your understanding and application of the material.
Collaborate with engineers:
Engage with engineers and designers early in the project to ensure the correct application of Aramid fiber.
Obtain proper training and certification:
Get trained and certified in handling, installation, and safety protocols associated with Aramid fiber.
Select reputable suppliers: Source Aramid fiber materials from trusted suppliers known for quality and reliability.
Follow manufacturer guidelines:
Adhere to guidelines for storage, handling, and installation of Aramid fiber to maintain its integrity.
Conduct thorough site preparation: Prepare the work area adequately, minimizing exposure to moisture during installation.
Ensure proper equipment and tools:
Use appropriate tools for cutting, shaping, and installing Aramid fiber.
Maintain quality control: Implement quality control measures to ensure proper installation and compliance with specifications.
Communicate with the project team:
Maintain open communication with the project team to align on using Aramid fiber.
Follow safety protocols:
Adhere to protocols and guidelines when working with Aramid fiber.
Continuous learning and improvement:
Stay updated on industry advancements and best practices in working with Aramid Fiber.
Surface Preparation:
Ensure that the surface where the Aramid fiber will be applied is clean, dry, and free from any contaminants that may affect adhesion. Remove any loose particles or debris from the surface.
Adhesive Selection: Choose an appropriate adhesive or resin system for bonding Aramid fiber to the substrate. Consider factors such as compatibility, curing time, and required strength for the specific application.
Cutting and Shaping:
Use appropriate tools to cut the Aramid fiber to the desired dimensions. Take precautions to prevent fraying or damage to the fibers during cutting. Shape the fiber as needed to fit the contours of the surface or structure.
Mixing Adhesive or Resin:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing the adhesive or resin. Ensure thorough mixing to achieve proper curing and bonding.
Application Method:
Apply the adhesive or resin to the surface using a suitable method, such as brushing, rolling, or spraying. Ensure an even and consistent coverage, avoiding excessive buildup or pooling of adhesive.
Placing Aramid Fiber:
Place the pre-cut Aramid fiber onto the adhesive-coated surface, pressing it down gently to ensure good contact and adhesion. Use a roller or other appropriate tool to remove air bubbles or wrinkles.
Additional Layers: If multiple layers of Aramid fiber are required, repeat the process, applying adhesive or resin between each layer. Ensure proper alignment and consolidation of the layers.
Curing and Drying:
The adhesive or resin can cure or dry according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Provide the necessary temperature, humidity, and curing time to ensure optimal bonding and strength development.
Finishing and Surface Treatment:
Once the Aramid fiber application has cured, any necessary finishing or surface treatment can be performed. This may include sanding, shaping, or applying protective coatings as required.
Quality Control and Testing: Conduct thorough quality control inspections and testing to ensure the integrity and performance of the Aramid fiber application. Depending on the application requirements, this may involve visual inspection, non-destructive, or mechanical testing.
Maintenance and Care:
Provide proper maintenance and care for the Aramid fiber application, following any specific guidelines provided by the manufacturer. Regular inspections and necessary repairs or reapplication should be carried out to ensure continued performance.
- Establish a comprehensive quality control plan tailored to the Aramid fiber application.
- Clearly define acceptance criteria aligned with project specifications and industry standards.
- Maintain thorough documentation and record-keeping of quality control activities.
- Inspect incoming Aramid fiber materials for visible defects and compliance with requirements.
- Test the adhesive or resin system for compatibility and performance with Aramid fiber.
- Evaluate the surface preparation process for cleanliness, dryness, and smoothness.
- Inspect the application for proper alignment, adhesion, and coverage.
- Perform bonding strength tests to assess the integrity of the Aramid fiber application.
- Conduct visual inspections for defects, uniformity, and overall appearance.
- Consider non-destructive testing techniques to detect hidden defects or inconsistencies.
- Perform a final inspection to verify compliance with requirements and acceptance criteria.
- Continuously evaluate processes, implement improvements, and incorporate feedback for future applications.
technical documents
Photo Gallery
Technical documentation request
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Aramid Fibers?
Aramid Fibers are a type of synthetic fiber made from aromatic polyamides. Aramid Fibers were the first organic fibers with sufficient tensile strength and modulus to be used in advanced composites. These fibers are very resistant to heat and high temperatures. In addition, their tensile strength is almost five times that of steel. At the same time, it has a very low weight. For this purpose, it is used in various applications.
How are Aramid Fibers compared to carbon fibers?
The main difference between carbon fiber and Aramid Fibers is that aramid fiber is hard but carbon fiber is brittle. In addition, carbon fiber has a higher strength than aramid.
How are aramid fibers compared to glass fibers?
The tensile strength of aramid fibers is almost the same as the tensile strength of glass fibers. But the modulus of aramid fibers can be about twice that of glass fibers. In addition, glass fibers are heavier than heavy aramid fibers. In order to obtain a strength equal to the strength of glass fibers, half of the aramid fibers can be used to obtain the strength of the glass fiber sample.
What are the different trade names of aramid fibers?
Aramid fibers are available in different brands. Different brand names of Aramid Fibers are: Kevlar, Technora, Tawron, Nomex and ...
What are the different types of Aramid Fibers?
Aramid fibers are available in two different types, meta aramid and para aramid. Meta-aramid fibers have excellent thermal, chemical and radiation resistance. For this purpose, metaramides are used in fire-resistant textiles. Para-aramid fibers have a higher strength than meta-aramid fibers. For this purpose, para amides are used to strengthen civil structures.
What are the benefits of aramid fibers?
Aramid Fibers have good properties such as high strength, good abrasion resistance, good resistance to organic solvents, non-conductive, no melting point, low flammability, good integration at high temperatures, high yang modulus, etc.
What are the disadvantages of aramid fibers?
Disadvantages of Aramid Fibers include low moisture absorption, low adhesion to resins, sensitivity to ultraviolet rays and acids, relatively high cost, and so on.
What are the uses of aramid fibers?
Aramid Fibers are commonly used as reinforcing fibers for polymer-based composites. Other applications of aramid fibers include the manufacture of protective clothing, sails, car parts, aircraft fuselages, boat hulls, fiber optic and electromechanical cables, military applications, aerospace, ballistic protection applications such as bulletproof vests, etc...
With what resins are Aramid Fibers used?
Aramid Fibers are compatible with epoxy resin, vinyl ester resin and isophthalic polyester resin. But the best adhesion and best performance is provided by epoxy resin.









































Be the first to review “Aramid Wrap AFRP”