PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
What is PP fiber?
PP fibers, also known as polypropylene fibers, are synthetic fibers made from polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer. These fibers are used as reinforcing material in concrete and other construction applications. PP fibers, such as monofilament or fibrillated, are available in various lengths and forms to suit different requirements.
PP fibers are added to concrete mixes to improve their properties and performance. When mixed into concrete, these fibers disperse throughout the mixture, forming a three-dimensional network that enhances the concrete’s tensile strength, toughness, and durability. The fibers act as a reinforcement by reducing crack formation and controlling crack propagation, improving the overall structural integrity of the concrete.
The use of PP fibers in concrete offers several advantages. They provide improved resistance against shrinkage cracking, impact, and fatigue. They also enhance the resistance of concrete to temperature variations, minimizing the potential for thermal cracking. PP fibers are non-corrosive, meaning they do not rust or degrade over time, making them suitable for long-term applications.
PP fibers find application in various concrete structures, including slabs, floors, pavements, shotcrete, precast elements, and more. They are commonly used in situations where control of cracking and improved performance of concrete is desired.
Polypropylene Fibers in Various Industries
Polypropylene fibers, also known as PP fibers, are a type of chemical fibers widely used in various industries. They rank fourth in global production, following polyesters, polyamides, and acrylics. With an annual production rate of around 4 million tons, these fibers have gained prominence since their first application by the US Corps of Engineers in 1965 for blast-resistant concrete.
Properties and Production of Polypropylene Fibers
Over time, the utilization of PP fibers has increased, particularly for concrete reinforcement through compression. Incorporating these fibers into concrete enhances its tensile strength, bending strength, stiffness, impact resistance, and fracture behavior. Compared to steel fibers, PP fibers require a lower percentage for effective reinforcement. Additionally, the resistance of PP fibers can be enhanced during production using fans. With a density of approximately 0.9 grams per cubic centimeter, these fibers exhibit high hardness due to their crystalline nature, characterized by irregular molecules. They also demonstrate excellent resistance to chemical attacks and bacteria, with a crystallinity level of around 70%.
Engineering Plastic and Unique Characteristics of Polypropylene Fibers
When combined with ethylene, a more rigid and flexible material, polypropylene fibers form a product known as engineering plastic. While unpigmented PP fibers are somewhat transparent, they are typically manufactured with a matte finish and can be colored for aesthetic purposes. These fibers exhibit excellent fatigue resistance.
Advantages of Polypropylene Fibers in Concrete Applications
One notable advantage of using PP fibers in concrete is their compatibility, enabling concrete to acquire fiber properties. Another benefit is their chemical neutrality, which enhances the resistance of PP fiber-reinforced concrete to chemical attacks. Unlike other compressed fibers, PP fibers do not agglomerate when mixed with concrete. Being hydrophobic, PP fibers do not absorb water from the cement paste during mixing, eliminating the need to adjust the water content of the concrete to accommodate the fibers. Additionally, these fibers, like others, do not require concrete cover.
Production and Application of Polypropylene Fibers in Construction
Polypropylene fibers, or concrete PP fibers, are produced through the chain polymerization of propene monomers using the melt-spinning process. They possess exceptional hardness, stability, and heat resistance and exhibit antistatic, non-magnetic, and non-conductive properties. Furthermore, their long lifespan, lack of odor, and skin-friendliness make them suitable for food, pharmaceutical, and healthcare applications. PP fibers are environmentally friendly and harmless.
In construction, PP fibers are an ideal reinforcement material for concrete and mortar applications. Their use delays shrinkage crack formation, reduces crack width and enhances energy absorption and fire resistance properties. Notably, using polypropylene fibers can reduce or eliminate the need for traditional reinforcement materials like steel, resulting in improved durability and stability of structures.
The advantages of employing polypropylene fibers in construction include their affordable cost, versatility in various applications, and lower specific weight compared to other plastic materials, requiring a smaller quantity to achieve desired characteristics.
Determining the Appropriate amount of Polypropylene Fibers
Determining the appropriate number of polypropylene fibers depends on the specific type used. For filament microfibers, a dosage of 0.3 to 0.45 kg per cubic meter of concrete typically provides satisfactory performance. In mesh microfibers, the common dosage ranges from 0.45 to 0.89 kg/m³.
Methods of Incorporating Polypropylene Fibers into Concrete
Polypropylene fibers can be incorporated into concrete using either a mixer or manual mixing. In both methods, the fibers are added to the concrete mixture along with water and other components, ensuring uniform distribution before proceeding with normal work conditions.
Growth Rate of Polypropylene Fibers
The market size for polypropylene fibers exceeded 3.5 billion dollars in 2020, with the price of polypropylene concrete fibers averaging around 945 dollars per ton. It is anticipated to experience significant growth, surpassing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3% from 2021 to 2027, with a projected price of over $130,000 per kilo. The increasing global population, improved economic conditions, evolving living standards, the rapid growth of industrial activities (especially in emerging economies), and demand for durable and lightweight products in industries such as automotive manufacturing and construction are the key drivers of the production and sale of polypropylene fibers.
Afzir Company, a Leading Provider of Polypropylene Fibers
Afzir Company, a reputable supplier of concrete fibers, including polypropylene fibers, has years of experience in this field. They offer a wide range of concrete fibers and provide the convenience of purchasing them online. To inquire about prices and receive a price list for concrete and PP fibers, contact their experts or leave a message on WhatsApp. Their knowledgeable team will guide you promptly to help you choose suitable polypropylene fibers for your project.
Features
- Non-magnetic
- No dust absorption
- Resistant to bases
- Safe and easy to use
- Affordable price
- Reduction and removal of concrete surface cracks
- Increased wear resistance
- Enhanced resistance to thawing and freezing cycles
- Improved impact resistance
Applications
- Industrial concrete floors with high and low traffic
- Concrete exposed to dynamic loads and fire
- Motorized roads and pavements
- Retaining walls and slope-guarding structures
- Machinery foundation
- Reservoirs, pools, and marine structures
- Production of cement or Iranite sheets
- Construction of concrete wall coverings (Romalin)
Packaging
- 20 kgs bags
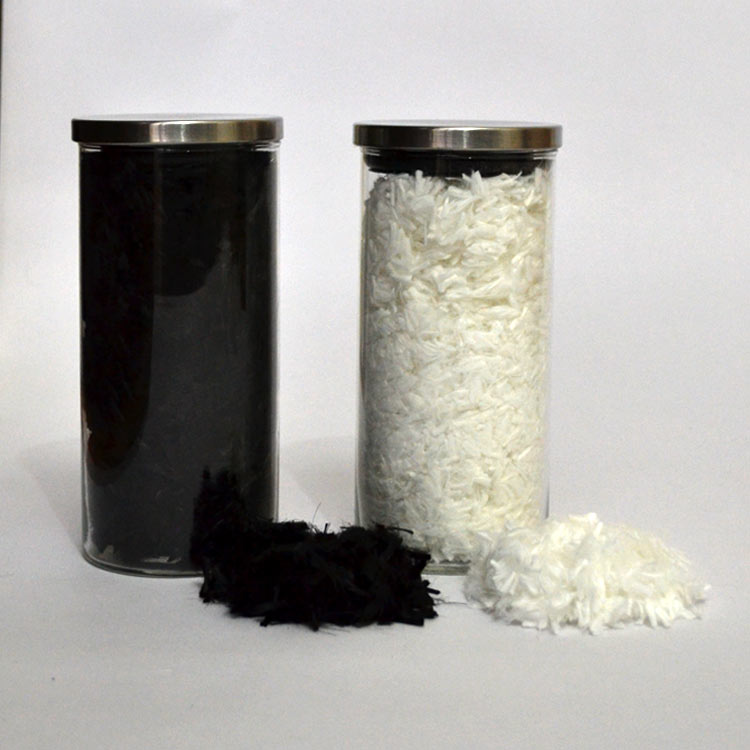
Colour
- Black
- White
technical specifications
| color |
Black and white |
| material |
polypropylene |
| Fiber length |
6 – 12 mm |
| density |
0.9gr/cm³ |
| Fiber thickness |
3-6denier |
| Tensile strength |
400MPa |
| elongation |
0.8% |
| melting temperature |
165 ℃ |
- Understand the Properties: Familiarize yourself with the specific properties of polypropylene fibers, such as non-magnetism, dust resistance, and chemical resistance.
- Determine Optimal Dosage: Experiment and determine the appropriate amount of polypropylene fibers for each application.
- Proper Fiber Distribution: Ensure thorough and uniform distribution of polypropylene fibers within the concrete mixture.
- Consider Fiber Length: Select the appropriate fiber length based on the application’s requirements.
- Quality Control: Implement a robust system to ensure consistent fiber quality.
- Compatibility with Admixtures: Consider the compatibility of polypropylene fibers with other concrete admixtures.
- Proper Concrete Placement and Curing: Follow standard concrete placement and curing practices.
- Document Performance and Learn from Experience: Keep records of project-specific details and evaluate long-term performance for future improvement.
- Stay Updated with Research and Innovations: Stay informed about the latest research and innovations related to polypropylene fibers.
- Collaborate with Suppliers and Experts: Establish relationships with reputable suppliers and seek their expertise for guidance during project implementation.
- Understand the Purpose: Contractors should clearly understand why polypropylene fibers are being used in concrete and the benefits they provide.
- Communication with Engineers: Effective communication with engineers or designers is crucial to ensure the proper implementation of polypropylene fibers according to project specifications.
- Proper Handling and Storage: Contractors should follow manufacturer guidelines for handling and storing polypropylene fibers to maintain their quality and effectiveness.
- Adequate Mixing: Thorough mixing of polypropylene fibers with the concrete mixture is essential to achieve uniform dispersion throughout the project.
- Equipment and Tools: Contractors should use appropriate equipment and tools during the mixing and placement of concrete to prevent damage or loss of fibers.
- Training and Education: Training workers on proper handling, mixing, and placement techniques specific to polypropylene fibers can ensure successful implementation.
- Quality Control: Implementing a quality control system helps monitor the correct dosage and distribution of polypropylene fibers in concrete, ensuring desired results.
- Site Conditions: Contractors should consider site-specific conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals to optimize the performance of polypropylene fibers.
- Documentation: Maintaining detailed records of polypropylene fiber usage, including dosage and mixing procedures, helps track progress and addresses any issues that may arise during construction.
- Collaboration with Suppliers: Close collaboration with reputable suppliers ensures the timely delivery of high-quality polypropylene fibers and supports addressing any concerns or challenges during the construction process.
- Amount of usage: The recommended dosage of polypropylene fibers in concrete is typically 0.9 kg/m3 or 0.1% of the concrete volume but can vary between 0.6 kg/m3 and 3 kg/m3.
- Modify Mixing Plan: Adjust the concrete mixing plan to account for the addition of polypropylene fibers, considering the amount of cement replaced by the fibers.
- Thorough Mixing: Use appropriate mixing equipment and techniques to ensure the polypropylene fibers are evenly dispersed throughout the concrete mixture.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer for optimal fiber performance, including recommended mixing time and equipment.
- Quality Control: Implement measures to monitor fiber dosage and distribution during mixing, ensuring consistent application.
- Adjust Cement-Water Ratio: Considering the fibers used, consider adjusting the water-cement ratio of the concrete mixture. Seek guidance from the manufacturer or materials engineer.
- Document Fiber Usage: Keep detailed records of the number of polypropylene fibers used in each concrete batch for tracking and consistency purposes.
- Consult with Engineers and Designers: Maintain open communication with project engineers and designers to ensure proper incorporation of polypropylene fibers in line with design requirements.
- Follow Safety Guidelines: Adhere to safety protocols when handling and mixing concrete with polypropylene fibers, including wearing appropriate personal protective equipment.
- Training and Education: Provide training to workers involved in the mixing and placement process to ensure proper handling and application of polypropylene fibers.
- Establish a Quality Control Plan: Develop a comprehensive quality control plan specific to using polypropylene fibers in concrete, outlining procedures and specifications.
- Fiber Dosage Verification: Regularly verify the dosage of polypropylene fibers during the mixing process to ensure it aligns with the recommended amount for optimal performance.
- Fiber Distribution: Monitor the distribution of fibers within the concrete mixture to ensure uniform dispersion and minimize clustering or clumping.
- Mixing Time and Equipment: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the appropriate mixing time and equipment to achieve proper fiber dispersion and bonding with the concrete matrix.
- Sample Collection: Collect representative samples of the fiber-reinforced concrete at regular intervals for testing and evaluation.
- Testing Methods: Utilize appropriate testing methods to assess the properties and performance of the fiber-reinforced concrete, such as compressive strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the fiber-reinforced concrete meets the required industry standards and specifications, including any specific guidelines related to polypropylene fiber usage.
- Document and Track Data: Maintain detailed records of the fiber dosage, mixing procedures, testing results, and any deviations or adjustments made during the quality control process.
- Training and Certification: Ensure that personnel in quality control procedures receive proper training and certification to perform the required tests accurately and consistently.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously evaluate and analyze the quality control data to identify any trends, issues, or areas for improvement and implement corrective actions as necessary.
technical documents
Photo Gallery
Technical documentation request
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of polypropylene fibers for concrete?
PP fibers or polypropylene fibers (PPF™ code) is one of the alternative materials for steel rebar for concrete reinforcement.
What are the advantages of using polypropylene fibers?
It is more economical than other fibers, it is easy and quick to implement, it is a good alternative to concrete reinforcement and it maintains the cohesion of the concrete mix by limiting the movement of solid particles.
What is the characteristic of polypropylene fibers?
Polypropylene fiber is a type of polymer material with light weight, high strength and corrosion resistance.
What colors are there in polypropylene fibers?
Polypropylene fibers are available in white and black.
What is the resistance of polypropylene fibers against chemical reactions?
Polypropylene fibers have very good chemical resistance.
How are polypropylene fibers obtained?
It is produced through chain growth polymerization of propylene monomer.









































Be the first to review “Polypropylene Fiber”